First Discovery of Helium: How the Sun Revealed a Hidden Element
When we think of helium, most of us imagine birthday balloons floating in the air or that funny high-pitched voice you get after inhaling a little (don’t try this too much, though!). But the story of helium’s first discovery is far more dramatic and fascinating than a party trick.
Did you know that helium was discovered on the Sun before it was ever found on Earth? Yes, you read that right! It’s the only element that was first spotted in outer space before humans managed to identify it down here on our planet.
This article takes you on a journey back in time to the 19th century, when scientists, armed with telescopes and spectroscopes, made one of the most exciting discoveries in chemistry and astronomy. Along the way, we’ll uncover fun facts, historical twists, student-friendly stories, and modern-day uses of helium.
So grab your curiosity helmets, let’s travel back to the day when helium first made its grand appearance in human history.
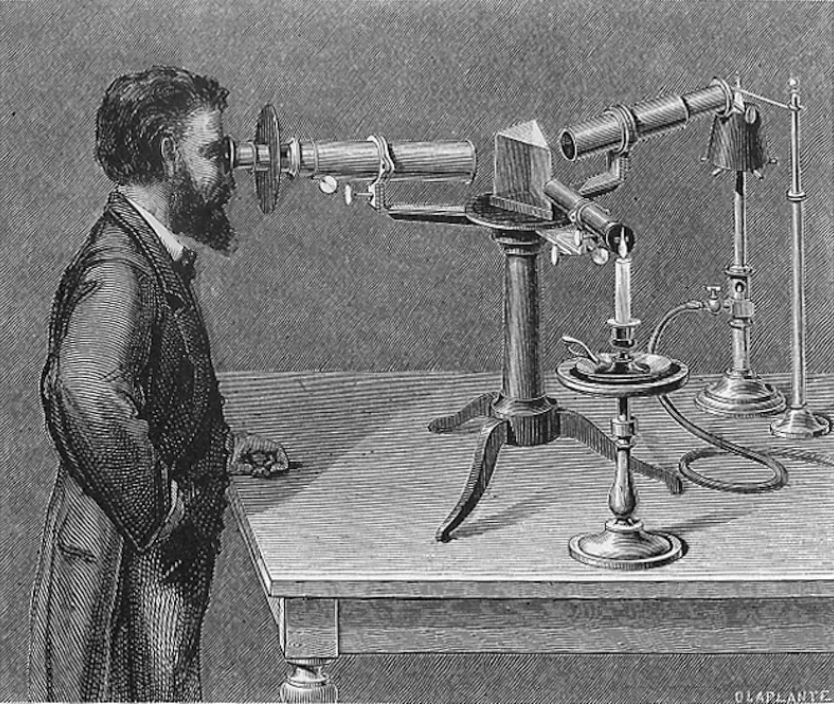
A Solar Eclipse That Changed Science Forever (1868)
The story begins on August 18, 1868, when a total solar eclipse swept across India. During this rare celestial event, two scientists, Pierre Janssen (France) and Norman Lockyer (England), were studying the Sun using a spectroscope.
What’s a Spectroscope?
Imagine a prism that splits sunlight into a rainbow of colors. Each element gives off light in a unique pattern of bright or dark lines called spectral lines. Think of it like fingerprints for atoms.
Janssen and Lockyer noticed something strange. Among the known lines of hydrogen and sodium, there was a new bright yellow line in the Sun’s spectrum at 587.6 nanometers.
At first, they thought it might be sodium, but it didn’t match! This meant it was something entirely new.
Lockyer’s Big Conclusion
Norman Lockyer boldly announced that this must be a new element not found on Earth yet. He named it “helium” after Helios, the Greek god of the Sun.
Fun Fact: Helium remains the only element first discovered in space before Earth!

The Search for Helium on Earth
After its solar debut in 1868, helium became a mystery element. Scientists knew it existed in the Sun, but could it also be hiding on Earth?
It took 27 years to find the answer.
- In 1895, Scottish chemist Sir William Ramsay discovered helium on Earth while heating up a uranium mineral called cleveite.
- When cleveite released gas, Ramsay analyzed it and found that it had the same spectral line as solar helium.
- At the same time, Swedish scientists Per Teodor Cleve and Nils Abraham Langlet confirmed helium in cleveite.
Finally, the Sun’s secret was revealed: helium was also part of Earth’s chemistry!
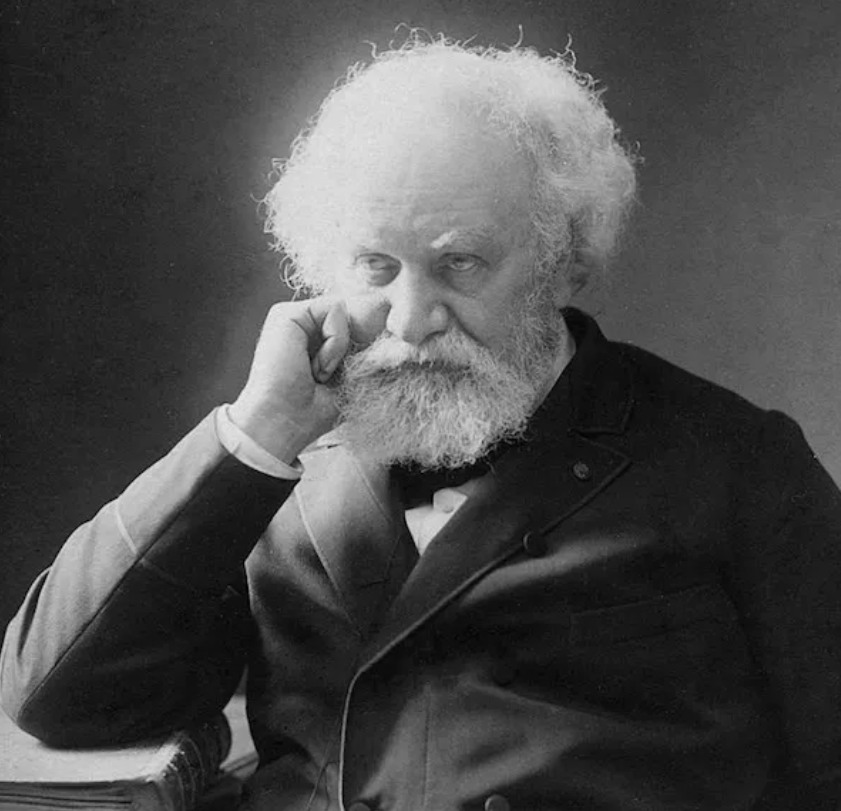
7 Fascinating Facts About the First Discovery of Helium
- Discovered in Space First: Helium is the only element first found outside Earth, on the Sun during an eclipse.
- Named After the Sun: The name “helium” comes from Helios, the Sun god in Greek mythology.
- Spectral Detective Work: It was found because of a yellow spectral line (D3 line) at 587.6 nm.
- Skeptics Mocked It: At first, many scientists didn’t believe helium existed, calling it “imaginary.”
- Found on Earth in 1895: Ramsay discovered helium in the uranium mineral cleveite.
- Second Lightest Element: After hydrogen, helium is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the universe.
- Party Balloons to Rocket Fuel: What was once just a mysterious solar element is now used in MRI machines, rockets, fiber optics, and balloons!
Scientific Importance of Helium’s Discovery

The discovery of helium was more than just a curiosity. It had huge impacts on astronomy, chemistry, and physics.
- Proof of Spectroscopy Power: It showed that scientists could identify elements not just on Earth, but also in stars and space.
- Astronomy Breakthrough: Opened the door to astrophysics, allowing us to study stars by their light.
- Chemistry Expansion: Added a new noble gas to the periodic table, later joined by neon, argon, krypton, and xenon.
- Nuclear Fusion Understanding: Helium turned out to be the main product of hydrogen fusion in stars, helping us understand how the Sun shines.
Why Students Should Love Helium’s Story
Helium’s discovery story has everything a student loves:
- Adventure: A solar eclipse in India.
- Mystery: A hidden element not found on Earth yet.
- Science Magic: Detecting something invisible using just light.
- Drama: Years of disbelief before acceptance.
It’s a perfect reminder that science is not just facts in a textbook; it’s a detective story filled with excitement, mistakes, and eventual breakthroughs.
Fun Classroom Idea: Teachers can show students a simple prism experiment to explain how spectroscopy works.
Helium Today: From Balloons to Space Rockets
Since its discovery, helium has gone from a mystery element to an essential part of modern life.
Everyday Uses of Helium:
- Balloons & Blimps: Helium is lighter than air, making balloons float. Unlike hydrogen, it’s non-flammable (safer for blimps).
- Medical Tech: Used in MRI scanners to cool magnets.
- Science Labs: Superconducting magnets and cryogenics.
- Space Exploration: NASA uses helium to pressurize rocket fuel tanks.
- Fiber Optics & Electronics: Helium is vital in manufacturing microchips and fiber optic cables.
Fun Fact: Your voice goes high-pitched when you inhale helium because sound travels faster in helium than in air, changing resonance in your vocal cords!
Timeline of Helium’s Discovery
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1868 | Janssen & Lockyer observe unknown yellow spectral line during solar eclipse → Helium first discovered on the Sun. |
| 1871 | Scientists debate existence; some dismiss it as “imaginary.” |
| 1895 | Sir William Ramsay discovers helium on Earth in cleveite mineral. |
| 1903 | Large natural helium reserves found in natural gas fields in the USA. |
| 20th Century | Helium becomes critical for airships, science, and technology. |
| Today | Essential in medicine, space, tech, and research. |
Helium’s Global Importance
- US Helium Reserves: The U.S. holds the world’s largest helium reserves, especially in Texas.
- Helium Shortages: Despite being the universe’s second most abundant element, helium is rare on Earth because it escapes into space.
- International Demand: Used heavily in China, Japan, and Europe for science and industry.
Conclusion
The first discovery of helium is not just about finding an element; it’s about the spirit of science itself.
From a mysterious yellow line during an eclipse in India to being one of the most useful elements in modern technology, helium’s journey is full of wonder.
It teaches us:
- Science is about curiosity, patience, and open-mindedness.
- Discoveries often come from unexpected places (like the Sun!).
- Even “fun” elements like helium have serious roles in medicine, space, and technology.
So the next time you see a balloon floating at a birthday party, remember: that gas inside was once a cosmic mystery hidden in the heart of the Sun.
The story of helium’s first observation is more than just a science chapter; it’s a reminder of human curiosity, imagination, and discovery. From being spotted in the Sun’s spectrum during a solar eclipse to becoming a lifesaving and space-exploring element on Earth, helium continues to shape the way we understand the universe.
Want to dive deeper into fascinating science stories like this?
Subscribe to our newsletter for daily science facts and discoveries.
Bookmark our website to never miss an update.
Share this article with your friends and students to spread the joy of learning.
Because every element has a story, and helium’s is just the beginning.
1. When was helium first observed?
Helium was first observed on August 18, 1868, during a solar eclipse in India by French astronomer Jules Janssen and later confirmed by British astronomer Norman Lockyer.
2. Why is it called helium?
The name helium comes from the Greek word “Helios”, meaning the Sun, because it was first discovered in the Sun’s spectrum before being found on Earth.
3. Who discovered helium on Earth?
Helium was first isolated on Earth in 1895 by Sir William Ramsay in London, when he treated a mineral called cleveite with acid and detected helium gas.
4. Why was helium’s discovery so special?
Helium was the first element ever discovered in space before being found on Earth, making it a unique case in the history of chemistry and astronomy.
5. What are some fun facts about helium?
Helium is the second lightest element after hydrogen.
It is the only element that doesn’t solidify at normal pressure, even at absolute zero.
Helium makes your voice sound “squeaky” because sound travels faster through it.
It is used in MRI machines, space rockets, and balloons.
6. How is helium used today?
Helium is widely used in medical technology (MRI scanners), cryogenics, welding, space exploration, semiconductors, and as a cooling medium. Its unique properties make it indispensable in modern science and industry.
7. Is helium rare on Earth?
Yes, helium is relatively rare on Earth. Unlike other gases, it doesn’t chemically bond with anything, and because it’s so light, it often escapes into space. That’s why helium supplies are limited and valuable.
8. Why do helium balloons float?
Helium balloons float because helium is lighter than air. The surrounding air is denser, so the balloon rises upward.
9. Can we run out of helium?
Yes, helium is a non-renewable resource on Earth. Most helium comes from natural gas fields, and once it escapes into the atmosphere, it drifts into space, making conservation critical.
10. What makes helium important for science?
Helium plays a vital role in superconductivity, quantum research, nuclear reactors, and space exploration. Without helium, many technologies that we rely on daily would not function efficiently.